There can be 4 cases of latch-to-flop timing paths as discussed below:
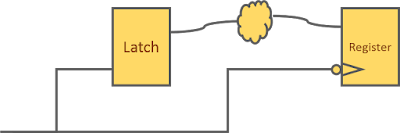
1. Positive level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered register: Figure 1 below shows a timing path being launched from a positive level-sensitive latch and being captured at a positive edge-triggered register. In this case, setup check will be full cycle with zero-cycle hold check. Time borrowed by previous stage will be subtracted from the present stage.
 |
| Figure 1: Positive level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered register timing path |
Timing waveforms corresponding to setup check and hold check for a timing path from positive level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered register is as shown in figure 2 below.
 |
| Figure 2: Setup and hold check waveform for positive latch to positive register timing path |
2. Positive level-sensitive latch to negative edge-triggered register: Figure 3 below shows a timing path from a positive level-sensitive latch to negative edge-triggered register. In this case, setup check will be half cycle with half cycle hold check. Time borrowed by previous stage will be subtracted from the present stage.
Timing waveforms corresponding to setup check and hold check for timing path starting from positive level-sensitive latch and ending at negative edge-triggered register is shown in figure 4 below:
 |
| Figure 4: Setup and hold check waveform for timing path from positive latch to negative register |
3. Negative level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered register: Figure 5 below shows a timing path from a negative level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered register. Setup check, in this case, as in case 2, is half cycle with half cycle hold check. Time borrowed by previous stage will be subtracted from the present stage.
Timing waveforms for path from negative level-sensitive latch to positive edge-triggered flop are shown in figure 6 below:
 |
| Figure 6: Waveform for setup check and hold check corresponding to timing path from negative latch to positive flop |
4. Negative level-sensitive latch to negative edge-triggered register: Figure 7 below shows a timing path from negative level-sensitive latch from a negative edge-triggered register. In this case, setup check will be single cycle with zero cycle hold check. Time borrowed by previous stage will be subtracted from present stage.
Figure 8 below shows the setup check and hold check waveform from negative level-sensitive latch to negative edge-triggered flop.
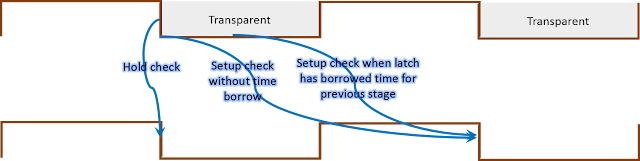 |
| Figure 8: Timing waveform for path from negative latch to negative flip-flop |