What are lock-up latches: Lock-up
latch is an important element in scan-based designs, especially for
hold timing closure of shift modes. Lock-up latches are necessary to avoid skew
problems during shift phase of scan-based testing. A lock-up latch is nothing
more than a transparent latch used intelligently in the places where clock skew
is very large and meeting hold timing is a challenge due to large uncommon
clock path. That is why, lockup latches are used to connect two flops in scan
chain having excessive clock skews/uncommon clock paths as the probability of
hold failure is high in such cases. For instances, the launching and capturing
flops may belong to two different domains (as shown in figure below).
Functionally, they might not be interacting. Hence, the clock of these two
domains will not be balanced and will have large uncommon path. But in
scan-shift mode, these interact shifting the data in and out. Had there been no
lockup latches, it would have been very difficult for STA engineer to close
timing in a scan chain across domains. Also, probability of chip failure would
have been high as there a large uncommon path between the clocks of the two
flops leading to large on-chip-variations. That is why; lockup latches can be referred as as the soul mate of scan-based designs.
 |
|
Figure 1 : Lockup latches - the soul
mate of scan-based designs
|
Where to use a lock-up
latch: As mentioned above, a lock-up latch is used where
there is high probability of hold failure in scan-shift modes. So, possible
scenarios where lockup latches are to be inserted are:
- Scan chains from different clock domains: In this case, since, the two domains do not interact functionally, so both the clock skew and uncommon clock path will be large.
- Flops within same domain, but at remote places: Flops within a scan chain which are at remote places are likely to have more uncommon clock path.
 |
|
Figure
2: A path crossing from domain
1 to domain 2 (scope for a lock-up latch insertion)
|
 |
|
Figure
3: Timing diagram showing setup and
hold checks for path crossing from domain 1 to domain 2
|
Positive or negative level
latch?? It depends on the path you are inserting a
lock-up latch. Since, lock-up latches are inserted for hold timing; these are not
needed where the path starts at a positive edge-triggered flop and ends at a
negative edge-triggered flop. It is to be noted that you will never find scan paths originating at positive edge-triggered flop and ending at negative edge-triggered flop due to DFT specific reasons. Similarly, these are not needed where path starts
at a negative edge-triggered flop and ends at a positive edge-triggered flop.
For rest two kinds of flop-to-flop paths, lockup latches are required. The
polarity of the lockup latch needs to be such that it remains open during the
inactive phase of the clock. Hence,
- For flops triggering on positive edge of the clock, you need to have latch transparent when clock is low (negative level-sensitive lockup latch)
- For flops triggering on negative edge of the clock, you need to have latch transparent when clock is high (positive level-sensitive lockup latch)
Who inserts a lock-up latch:
These days, tools exist that automatically add lockup latches where a scan
chain is crossing domains. However, for cases where a lockup latch is to be
inserted in an intra-domain scan chain (i.e. for flops having uncommon path),
it has to be inserted during physical implementation itself as physical
information is not feasible during scan chain implementation (scan chain
implementation is carried out at the synthesis stage itself).
Which clock should be connected to lock-up latch: There are two possible ways in which we can connect the clock pin of the lockup latch inserted. It can either have same clock as launching flop or capturing flop. Connecting the clock pin of lockup latch to clock of capturing flop will not solve the problem as discussed below.
Which clock should be connected to lock-up latch: There are two possible ways in which we can connect the clock pin of the lockup latch inserted. It can either have same clock as launching flop or capturing flop. Connecting the clock pin of lockup latch to clock of capturing flop will not solve the problem as discussed below.
- Lock-up latch and capturing flop having the same clock (Will not solve the problem): In this case, the setup and hold checks will be as shown in figure 5. As is apparent from the waveforms, the hold check between domain1 flop and lockup latch is still the same as it was between domain 1 flop and domain 2 flop before. So, this is not the correct way to insert lockup latch.
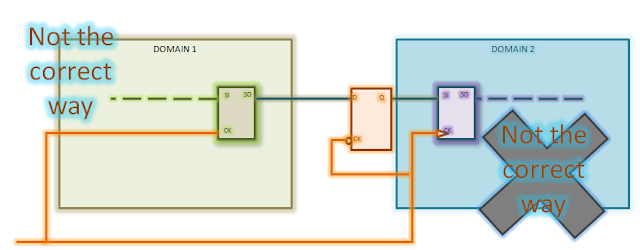 |
|
Figure
4: Lock-up latch clock pin
connected to clock of capturing flop
|
 |
|
Figure
5: Timing diagrams for figure 4
|
- Lock-up latch and launching flop having the same clock: As shown in figure 7, connecting the lockup latch to launch flop’s clock causes the skew to reduce between the domain1 flop and lockup latch. This hold check can be easily met as both skew and uncommon clock path is low. The hold check between lockup latch and domain2 flop is already relaxed as it is half cycle check. So, we can say that the correct way to insert a lockup latch is to insert it closer to launching flop and connect the launch domain clock to its clock pin.
 |
|
Figure
6: Lock-up latch clock pin
connected to clock of launch flop
|
 |
|
Figure
7: Waveforms for figure 6
|
Why don’t we add buffers: If
the clock skew is large at places, it will take a number of buffers to meet
hold requirement. In normal scenario, the number of buffers will become so
large that it will become a concern for power and area. Also, since
skew/uncommon clock path is large, the variation due to OCV will be high. So,
it is recommended to have a bigger margin for hold while signing it off for
timing. Lock-up latch provides an area and power efficient solution for what a
number of buffers together will not be able to achieve.
Advantages of inserting
lockup latches:
- Inserting lock-up latches helps in easier hold timing closure for scan-shift mode
- Robust method of hold timing closure where uncommon path is high between launch and capture flops
- Power efficient and area efficient
- It improves yield as it enables the device to handle more variations.
Lockup registers: Instead of latches, registers can also be used as lockup elements; however, they have their own advantages and disadvantages. Please refer to Lockup latches vs. lockup registers : what to chose for a comparative study of using lockup latches vs lockup registers.
References:
1) “Why not add buffer but lockup latch” - http://www.edaboard.com/thread82364.html
Also read:
- Setup and hold checks for latch-to-flop and flop-to-latch paths
- Controllability and observability - the two DFT principles
- On-chip variations - the STA takeaway
- Setup and hold - basics of timing analysis
- Interesting problem - latches in series
